Drafting Employment Contracts in Nigeria

by Counseal Team
Updated April 21, 2025

Starting a business is exciting—you have big ideas, ambitious goals, and a vision to make an impact. But beyond the hustle and innovation, there’s a crucial element that keeps your business running smoothly: solid legal foundations. One of the most important yet often overlooked aspects? Employment contracts.
Starting a business is exciting—you have big ideas, ambitious goals, and a vision to make an impact. But beyond the hustle and innovation, there’s a crucial element that keeps your business running smoothly: solid legal foundations. One of the most important yet often overlooked aspects? Employment contracts.
Think of them as the backbone of your workforce—clearly defining roles, responsibilities, rights, and expectations for both employers and employees. A well-drafted employment contract not only protects your business but also fosters trust, minimizes disputes, and ensures compliance with Nigerian labor laws. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know to create airtight employment contracts that safeguard both your company and your team.
Why Employment Contracts Matter
Think of employment contracts as your company’s safety net. They outline the terms of employment, protect both employer and employee rights, and help avoid misunderstandings. In Nigeria’s dynamic business environment, having robust employment contracts isn’t just smart—it’s essential for sustainable growth.
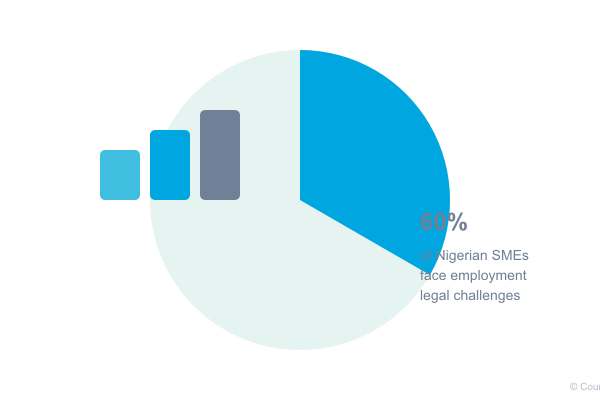
According to recent data from the International Labour Organisation, 60% of SMEs in Nigeria face legal challenges related to employment issues. This significant statistic underscores the importance of proper employment documentation. Moreover, well-structured employment contracts can enhance your company’s appeal to international investors and partners, particularly as Nigeria continues to attract global attention as Africa’s largest economy.
Navigating Nigerian Employment Law
The Nigerian employment law framework provides essential guidance for businesses of all sizes. Let’s break down the key elements you need to understand to ensure compliance and protect your business interests.
Understanding the Basics
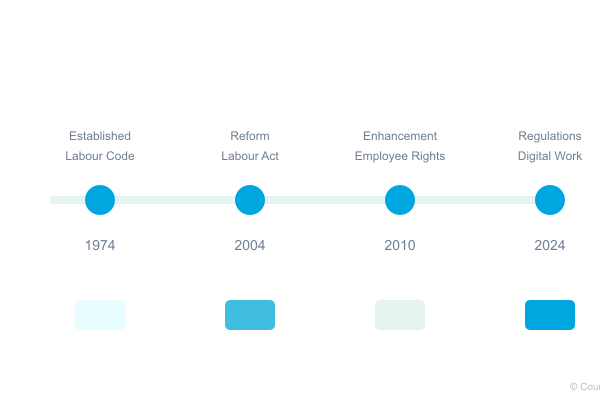
The Labour Act of 2004 serves as the foundation for employment relationships in Nigeria. This comprehensive legislation sets minimum standards for employment conditions, covering essential aspects from working hours to termination procedures. For business owners, understanding these fundamentals is crucial for building compliant and sustainable operations.
Key requirements under the Labour Act include:
- Written documentation of employment terms
- Clear specification of wages and payment terms
- Defined working hours and leave entitlements
- Proper termination procedures
Recent developments in Nigerian employment law have introduced additional protections for employees and obligations for employers. These changes reflect Nigeria’s commitment to maintaining international labor standards while addressing local business needs.
What is an Employment Contract?
Definition and Significance
An employment contract serves as a legally binding agreement between employer and employee, establishing the foundation for their professional relationship. It’s more than just a document—it’s your business’s first line of defense against potential disputes and misunderstandings.
In the Nigerian context, a well-crafted employment contract:
- Protects both parties’ interests
- Ensures compliance with local labor laws
- Establishes clear performance expectations
- Provides a framework for dispute resolution
Legal Requirements in Nigeria
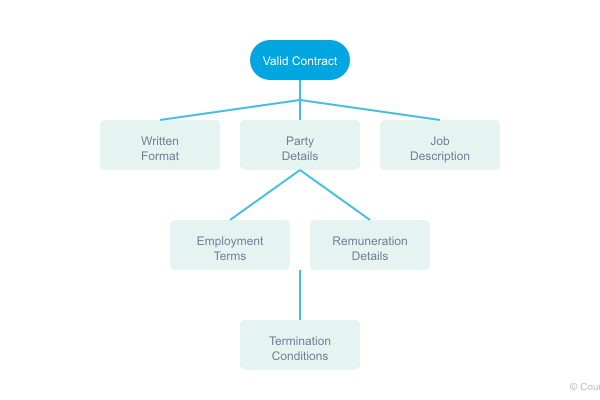
According to Nigerian law, employment contracts must meet specific requirements to be considered valid. These include:
- Written format (verbal agreements are insufficient)
- Clear identification of both parties
- Detailed job descriptions and responsibilities
- Specific terms of employment
- Remuneration details and payment terms
- Termination conditions
Types of Employment Contracts
Understanding different contract types helps you choose the right option for your business needs while ensuring compliance with Nigerian labor laws.
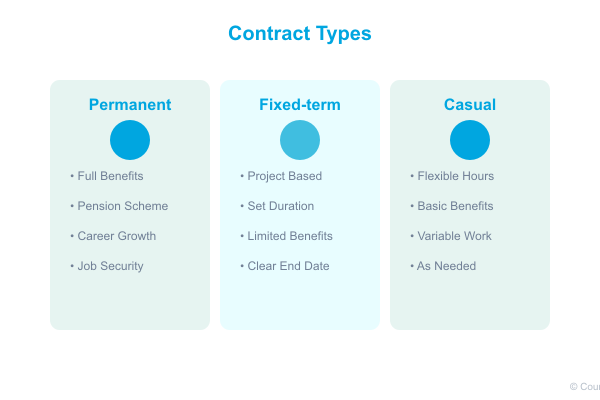
Permanent Contracts
Permanent contracts offer ongoing employment with no specified end date. These contracts typically include:
- Full benefits package
- Pension scheme participation
- Career development opportunities
- Long-term job security
Fixed-term Contracts
Fixed-term contracts specify a clear end date or project completion milestone. They’re particularly useful for:
- Project-based work
- Seasonal operations
- Market testing periods
- Temporary replacements
Casual and Part-time Contracts
These flexible arrangements suit specific business needs while maintaining legal compliance:
- Clear work schedules
- Proportional benefits
- Defined scope of work
- Specific duration terms
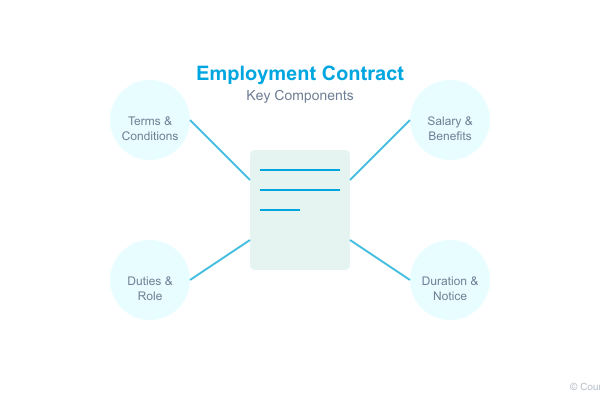
Key Components of Employment Contracts
Essential Clauses
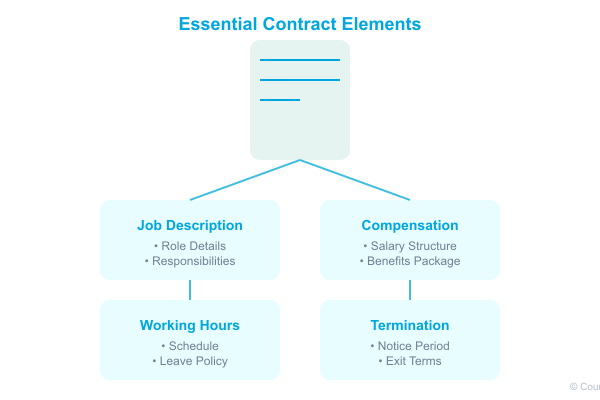
Job Description and Duties
A comprehensive job description should include:
- Detailed role responsibilities
- Reporting relationships
- Performance expectations
- Growth opportunities
Compensation and Benefits
Clear compensation terms covering:
- Base salary structure
- Bonus arrangements
- Health insurance details
- Pension contributions
- Other benefits
Working Hours and Leave Entitlements
Specific details about:
- Standard working hours
- Overtime policies
- Annual leave allocation
- Public holiday provisions
- Sick leave terms
Termination and Notice Periods
Clear guidelines for:
- Notice requirements
- Termination conditions
- Exit procedures
- Final settlement terms
Optional Clauses
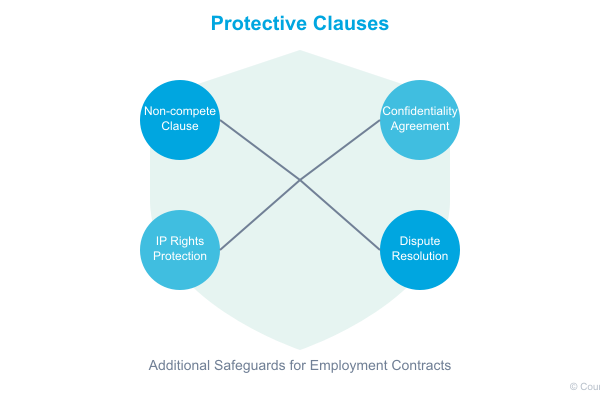
Non-compete and Confidentiality Agreements
Protection measures including:
- Scope of confidentiality
- Duration of restrictions
- Geographic limitations
- Industry-specific constraints
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Clear procedures for:
- Internal grievance handling
- Mediation processes
- Arbitration options
- Legal recourse paths
Compliance with Nigerian Labour Laws

Overview of Relevant Labour Laws
Essential legislation includes:
- Labour Act
- Employees’ Compensation Act
- National Minimum Wage Act (2024 amendments)
- Industrial Training Fund Act
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Contract Terms Ambiguity
Prevent confusion by:
- Using clear language
- Defining technical terms
- Providing specific examples
- Including measurement criteria
Statutory Compliance Failures
Ensure adherence to:
- Minimum wage requirements
- Working hour regulations
- Leave entitlements
- Safety standards
Practical Steps for Drafting Employment Contracts
Identifying Business Needs
Consider:
- Role requirements
- Department structure
- Growth plans
- Budget constraints
Drafting Clear Terms
Focus on:
- Simple language
- Specific details
- Measurable criteria
- Legal compliance
Review and Finalization
Ensure:
- Legal review
- Stakeholder input
- Compliance check
- Final approval
Seeking Legal Advice
Professional legal guidance ensures:
- Full compliance
- Risk mitigation
- Updated terms
- Protected interests
Recap of Key Points
Final Tips
Remember to:
- Regularly review contracts
- Update terms as needed
- Maintain clear records
- Seek professional advice
In Conclusion
For more detailed guidance on drafting employment contracts and other entrepreneurial insights, visit counseal.com/start. We offer comprehensive resources tailored for Nigerian entrepreneurs, helping you build strong foundations for sustainable business growth.
Happy drafting, and here’s to your success!