Force Majeure Clauses in Nigerian Contracts: A Comprehensive Guide

by Counseal Team
Updated February 14, 2025

Force majeure, meaning “superior force” in French, provides a legal framework for contract parties to suspend or terminate obligations when extraordinary circumstances arise. In Nigerian law, while not explicitly codified in statutory provisions, force majeure operates under common law principles, requiring careful drafting and interpretation.
Understanding Force Majeure in Nigerian Law
Force majeure, meaning “superior force” in French, provides a legal framework for contract parties to suspend or terminate obligations when extraordinary circumstances arise. In Nigerian law, while not explicitly codified in statutory provisions, force majeure operates under common law principles, requiring careful drafting and interpretation.
What Constitutes Force Majeure in Nigeria?
Natural Events
- Floods, earthquakes, and other natural disasters
- Epidemics and pandemics (as demonstrated by COVID-19)
- Severe weather conditions affecting business operations
Human-Induced Events
- Wars and civil unrest
- Labour strikes and industrial actions
- Terrorism and sabotage
Government Actions
- Changes in laws or regulations
- Trade restrictions or embargoes
- Nationalisation of industries
- Currency devaluation impacts
Essential Elements of Force Majeure Clauses
Clear Definition of Events
Your force majeure clause must explicitly list qualifying events. The Nigerian case of African Reinsurance Corporation v. AIM Consultants Ltd emphasised that courts strictly interpret these clauses based on specifically listed events.
Notice Requirements
- Specify the timeframe for notification
- Detail the required format and content
- Outline the notification procedure
- Include acknowledgment protocols
Obligations During Force Majeure
Parties must:
- Take reasonable steps to mitigate damages
- Maintain clear communication
- Document all impacts and mitigation efforts
- Resume obligations when possible
Real-World Impact: COVID-19 Case Study
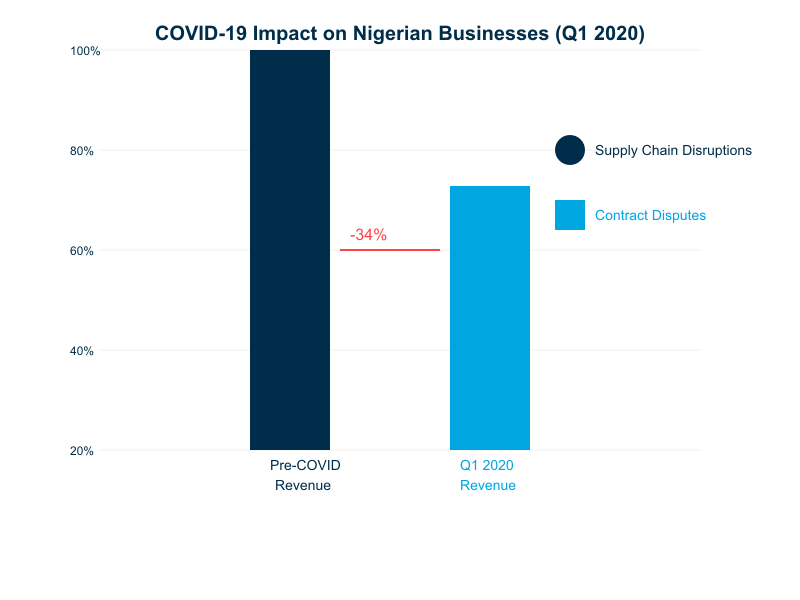
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly tested force majeure clauses in Nigerian contracts. According to the Nigerian Economic Summit Group, businesses experienced:
- 34% average revenue decline in Q1 2020
- Widespread supply chain disruptions
- Significant contract disputes
Practical Guidelines for Nigerian Entrepreneurs
Drafting Considerations
- Use precise language defining force majeure events
- Include modern risks like cyber attacks
- Specify the impact threshold requiring action
- Detail the procedure for claiming force majeure
Risk Assessment Steps
- Identify potential force majeure events specific to your industry
- Evaluate possible impacts on operations
- Develop mitigation strategies
- Review and update clauses regularly
Legal Framework and Enforcement
Nigerian courts consider several factors when enforcing force majeure clauses:
- Specific wording of the clause
- Causation between event and non-performance
- Mitigation efforts by affected party
- Proper notification compliance
Protecting Your Business Interests
Immediate Actions When Force Majeure Occurs
- Document the event and its impact
- Notify all relevant parties according to contract terms
- Implement mitigation measures
- Maintain detailed records
Long-term Strategies
- Regular contract reviews and updates
- Development of contingency plans
- Building flexible supply chains
- Maintaining strong stakeholder relationships
Get expert legal support for your contracts at counseal.com/start
Conclusion
Force majeure clauses serve as essential risk management tools in Nigerian contracts. Their effective implementation requires careful drafting, clear communication, and proactive management. As the business environment evolves, these clauses continue to adapt, protecting parties from unforeseen circumstances while maintaining commercial relationships.





