Navigating Employment and Labour Laws in Nigeria

by Counseal Team
Updated February 10, 2025

Understanding employment and labour laws is essential for both employers and employees in Nigeria. These laws establish the framework for workplace rights, responsibilities and relationships, ensuring fair treatment and legal compliance. Whether you’re an employer seeking to understand your obligations or an employee looking to protect your rights, this comprehensive guide will help you navigate Nigeria’s employment legislation with confidence.
Understanding employment and labour laws is essential for both employers and employees in Nigeria. These laws establish the framework for workplace rights, responsibilities and relationships, ensuring fair treatment and legal compliance. Whether you’re an employer seeking to understand your obligations or an employee looking to protect your rights, this comprehensive guide will help you navigate Nigeria’s employment legislation with confidence.
Why Understanding Employment Laws Matters
Nigeria’s position as Africa’s largest economy, with a labour force exceeding 90 million people, makes compliance with employment laws crucial. The Nigerian Labour Act serves as the primary legislation governing employment terms and conditions, including wages, working hours, and safety standards.
Recent data highlights the importance of compliance:
- 64% of Nigerian businesses faced legal challenges due to non-compliance with employment laws in 2020
- Companies with strong legal compliance report 30% higher employee retention rates
- Proper implementation of labour laws correlates with increased productivity and reduced workplace disputes
Understanding the Labour Act 2004
Scope and Application
The Labour Act primarily covers employees working under formal employment contracts. However, certain categories are exempt:
- Agricultural workers
- Family business employees without formal contracts
- Certain categories of domestic workers
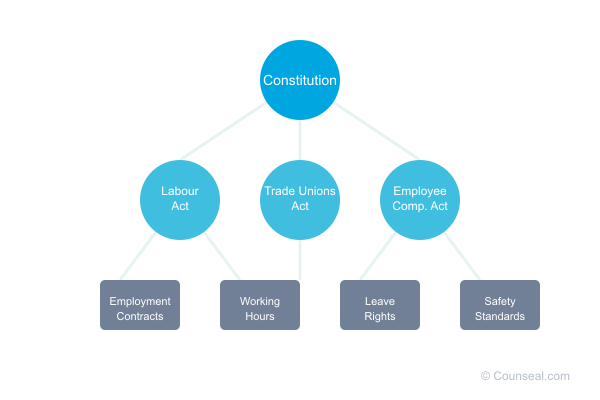
Key Provisions
Employment Contracts
The Act mandates clear documentation of employment terms, including:
- Job description and responsibilities
- Compensation and benefits
- Working hours and leave entitlements
- Termination procedures
Wages and Working Hours
- Standard working week: 48 hours maximum
- Overtime compensation requirements
- Regular wage payment schedules
- Current minimum wage: ₦70,000 (as of 2024)
Leave Entitlements
- Annual leave
- Sick leave
- Maternity leave
- Public holidays
The Employee Compensation Act 2010
Purpose and Coverage
The Employee Compensation Act provides protection for work-related injuries and occupational diseases. It establishes:
- Comprehensive injury compensation framework
- Medical expense coverage
- Wage replacement benefits
- Rehabilitation support
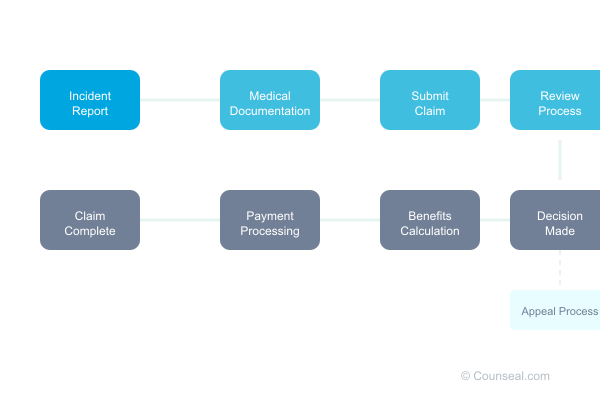
Claims Process
- Incident reporting requirements
- Medical documentation
- Claim submission procedures
- Benefits determination
- Appeal mechanisms
Types of Employment Contracts
Permanent Contracts
Permanent contracts offer:
- Job security
- Full benefits package
- Career development opportunities
- Pension contributions
- Health insurance coverage
Fixed-term Contracts
Key considerations include:
- Specific duration
- Renewal terms
- Termination provisions
- Benefits eligibility
- Performance metrics
Casual and Temporary Contracts
Important aspects:
- Flexible working arrangements
- Limited benefit entitlements
- Maximum duration restrictions
- Conversion requirements
- Worker protections
Employee Rights and Employer Obligations
Employee Rights
Fair Treatment
- Protection against discrimination
- Equal opportunity requirements
- Harassment prevention
- Grievance procedures
Safe Working Conditions
- Workplace safety standards
- Personal protective equipment
- Health monitoring
- Emergency procedures
Fair Remuneration
- Timely wage payment
- Minimum wage compliance
- Overtime compensation
- Benefit administration
Employer Obligations
Compliance Requirements
- Regular audits
- Documentation maintenance
- Policy implementation
- Training provisions
Record Keeping
- Employment contracts
- Payroll records
- Leave documentation
- Safety compliance
- Training records
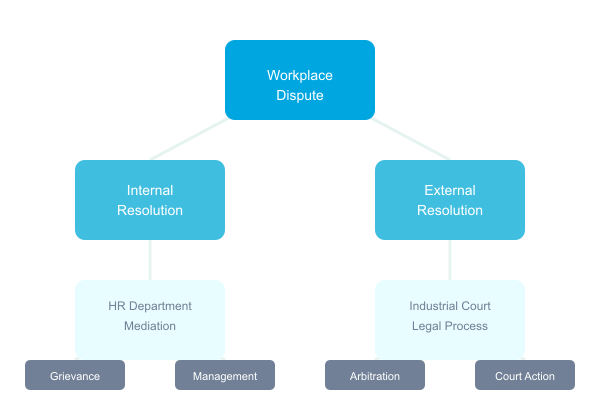
Dispute Resolution
Internal Resolution Mechanisms
- Grievance procedures
- Management review
- HR intervention
- Mediation options
External Resolution Options
- National Industrial Court proceedings
- Alternative dispute resolution
- Legal representation
- Appeals process
Conclusion
Effective navigation of Nigeria’s employment and labour laws requires ongoing attention to compliance and best practices. For entrepreneurs and business leaders, understanding these regulations is crucial for:
- Building sustainable businesses
- Maintaining positive workplace relationships
- Avoiding costly legal disputes
- Protecting both employer and employee interests
For professional guidance on employment law compliance and business protection, visit counseal.com/start.





