Definitive Guide: Personal Income Tax in Nigeria

by Counseal Team
Updated November 27, 2023
This article provides an in-depth knowledge of personal income tax in Nigeria, the applicable laws, administrative agencies, chargeable incomes, how personal income tax is accessed and charged as well as how to calculate the chargeable tax rates in Nigeria.
- What is personal income tax?
- What are the Laws regulating PIT in Nigeria
- Which Agencies administer Personal Income Tax in Nigeria?
- Chargeable and Nonchargeable incomes under the personal income tax in Nigeria
- How is personal income tax charged in Nigeria?
- What are the Personal income Tax Rates In Nigeria?
- What is the due date to file Personal Income Tax?
- What are the Penalties for failure to file or remit Personal Income Tax in Nigeria?
What is personal income tax?
Personal Income Tax (PIT) is a levy imposed by the federal or state government of Nigeria, on the income of certain individuals such as employees, partners in partnership, families or communities, which they are liable to pay to the relevant federal or state agencies where they reside in Nigeria.
Personal income tax is usually based on the source or residency rule.
What are the Laws regulating PIT in Nigeria
The Personal Income Tax (Amended) Act 2011 (PITA) and the Finance Act 2020 regulates the PIT.
These laws serve as a guide to individual and governmental agencies to understand the meaning of Personal Income Tax, the extent of its applicability, rates, it serves as a guide for administrative purposes.
Which Agencies administer Personal Income Tax in Nigeria?
Personal Income Taxes are paid to designated government agencies at the Federal or State level.
At the federal level, the Federal Inland Revenue Service (FIRS) administers personal income taxes at the Federal Capital Territory, while the State Board of Internal Revenue (SBIR) administers taxes at the various states in Nigeria.
Unlike what some might think, you shouldn’t pay your income tax directly to Banks.
Chargeable and Nonchargeable incomes under the personal income tax in Nigeria
Under the Personal Income Tax Act (PITA), there are chargeable and nonchargeable incomes in Nigeria
What are chargeable incomes?
Chargeable incomes include business or employment income of individuals whose income is taxable and determined by the Personal Income Tax Act (PITA). It is usually levied on the salaries or wages, dividends, interests or some other incomes of such persons, their expenses and other deductions in Nigeria, throughout an entire year.
What are nonchargeable incomes?
Non-chargeable incomes include income such as salaries or wages, interests or some other incomes of persons which cannot be tax in Nigeria, because of the reasons spelt out in section 37 schedule 6, part b and section 6 schedule 10 of the Personal Income Tax (Amended) Act 2011 (PITA) which deals with employment income of a person.
Personal Income Tax is chargeable on the income of the following individuals and they include:
- Income earners, partners in partnership, trust entities, unincorporated entities with an identifiable place in Nigeria,
- Non-resident individuals: in the case of an employee, if the employee has a Significant Economic Presence (SEP) in Nigeria, who are executing a trade which consist of: technical, professional, managerial, consultancy services, remotely for a person in Nigeria. (see PITA). However, the Act does not specify what makes up SEP but empowers the Minister of Finance to do so through an order.
- Executors or trustees, who habitually operate a trade through a person in Nigeria, authorized to conclude contracts on his behalf.
- Where an individual’s business involves a single contract for surveys, deliveries, installations, or constructions.
- Where an individual trade carries on trade is in a manner which in the opinion of the relevant tax authorities is deemed to be artificial.
- For an employee outside Nigeria, if the employer is in Nigeria.
Non-Chargeable Income under PITA
Individuals whose incomes are not chargeable or taxable include:
- Individuals whose duties are performed on behalf of an employer who is in a country other than Nigeria or fixed base employer who does not bear the remuneration of the employee in Nigeria.
- Individuals in employment, who are not in Nigeria for 183 days or more, inclusive of annual leave or temporary period of absence in a year.
- Individuals in employment, whose remuneration is taxable under the laws of other countries, this is to avoid Double Taxation Treaties (DTT) with that other country.
- Individuals whose employment is partly or wholly performed in Nigeria, but their remuneration is paid outside Nigeria.
- Individuals who earn the National Minimum wage, as spelt out by law in Nigeria to be N 30,000, or individuals who earn below the National Minimum wage. (This is contained in section 37 schedule 6 of the Personal Income Tax Act 2011 as amended).
It is important to note that there are benefits that cannot be taxed, such as retirement benefits of individuals, medical benefits, housing funds, etc, because these are the benefits of taxpayers.
It is important to state that every person is liable to a minimum income tax of 1% of their gross income, though aside those that earn the minimum wage or below it. (This is contained in section 37, schedule 6 of the PITA).
How is personal income tax charged in Nigeria?
Personal income tax can be accessed in two ways, either by pay-as-you-earn (PAYE) or self-assessment.
Personal income taxed by pay as you earn (PAYE scheme)
This is where the employer of an employee in an organization in Nigeria, deducts the tax of an employee monthly and remit to the relevant tax authorities in their state of residence.
Personal income taxed by self-assessment
This is where individuals who are self employed in Nigeria can access their taxes yearly, based on their income within that year. It must be remitted to the relevant tax authorities in their state of residence, and must be within the fiscal year or due date for filing tax returns as spelt out under the PITA.
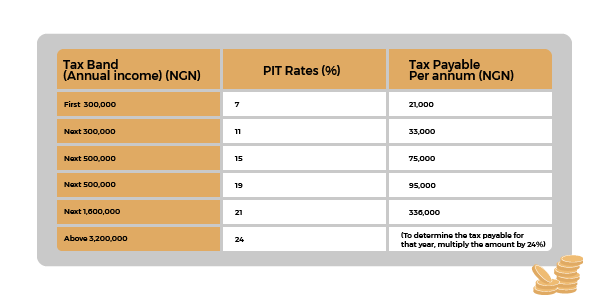
What are the Personal income Tax Rates In Nigeria?
Personal income tax rate is usually applied on a graduated scale and taxable income bands. It is calculated as set out in the table below.

How to calculate personal income tax rate in Nigeria
The PITA in Nigeria spells the applicable Tax rates as seen above. It usually progresses from 7% to 24% of the taxable income band. It usually progresses from 7% to 24% of the taxable income band.
To calculate the applicable tax rate, multiply the amount per annum by the tax rate as provided in the table above. For example, Jane earns N300,000.00 per annum, multiply N300,000.00 by 7% which is for the first year, this will amount to N21,000.00.
What is the due date to file Personal Income Tax?
Personal Income taxes are determined by the means in which they are charged.
If it is by pay as you earn (PAYE) as stated above, the due date of filing or payment is on or before the 10th day of the following due date for payment of salaries. For example, if Jane’s employer deducts her tax on the 10th of January 2022, it must be filed to the relevant tax authorities on or before the 10th day of February 2022.
In the second instance, which is self assessment, payment should be made along with returns within 90 days of the fiscal year, that is the year of remittance of filing of such taxes, not later than 31st March of the preceding year which is the following year. For example, the personal income tax of Jane for the year 2021, should be remitted or filed not later than 31st day of March 2022.
What are the Penalties for failure to file or remit Personal Income Tax in Nigeria?
The penalties for non-remittance or failure to file Personal income tax after the due dates is an imposition of an additional 10% of the taxable amount not being paid or filed.
Conclusion
It is important to file personal income tax before the due date, as tax compliant individuals are conferred with definite benefits, rights and privileges based on their tax compliance status, also they are exempted from the sanctions of noncompliance in Nigeria. Therefore seek a professional guide to know your chargeable personal income tax in Nigeria.





