How to Register a Company with CAC: A Practical Guide.

by Counseal Team
Updated November 26, 2023

The process of registering a business as a company is often viewed as rigid by business owners. In this guide, we walk you through, step by step, how to register your business as a company.
The Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC) recognises the various forms of business entities in Nigeria. These are as follows:
· Business name;
· Partnerships;
· Companies; and
· Incorporated Trustees.
A company is the most common form of business entity used by business owners. A business is recognised as a company by its registration with CAC. This practical guide defines a company, highlights the types of companies recognised by CAC, and how to register a company with CAC.
What is a Company in Nigeria?
A company is a recognised legal entity formed by at least two persons to carry out a business activity with the aim of making profit. CAC recognises the following types of companies as provided in the Companies and Allied Matters Act;
Limited Liability Company
The owners of this type of company are responsible for its debts only to the extent of the amount of capital they invested. This liability is further measured by shares and every owner’s liability is measured by the number of shares owned in the company. A Limited Liability company is of two types.
They are as follows:
Private Company Limited by Shares:
The shares of this company cannot be owned, traded, subscribed and exchanged publicly. This company is formed by a minimum of two persons and a maximum of fifty persons. Small and medium businesses often form this type of company as well as family-owned businesses.
Public Company Limited By Shares:
This limited liability company can be formed by two persons and more, as the number of persons who can form this company are unlimited. However, the shares of this company can be owned, traded, subscribed, and exchanged by members of the public. This is done by listing the company and its shares on the stock exchange for public trading.
Company Limited by Guarantee:
This type of the company is also known as a Guarantee Company. The owners of this company are known as guarantors. The liability of its owners are measured by the amount of money he/she is obliged to pay in the event that it is wound up. This type of company is often used by charitable organisations as they are not used for profitable ventures.
Unlimited Liability Company:
This type of company is uncommon in Nigeria. The liability of the members are unlimited as members assume full responsibility for all the debts of the company despite the capital invested.
The registration of any of these companies can be summarised into these three steps:
- Pre-Registration Step:
These are the preliminary steps to follow before proceeding to register a company. It includes creating an account on the CAC portal, selecting and reserving a name with the CAC. - Registration Step:
These are the steps to take to achieve registration. Here the business owner submits the details of the proposed company alongside the documents requested by the CAC on its portal. - Post-Registration.
These are steps to take after a certificate of registration has been issued to the company. These steps are necessary to ensure that the company is still a going concern.
Steps to Registering Your Company In Nigeria
The steps to registering a company are
Pre-Registration Steps;
The following steps highlighted below are steps a business owner should take before registering a company:
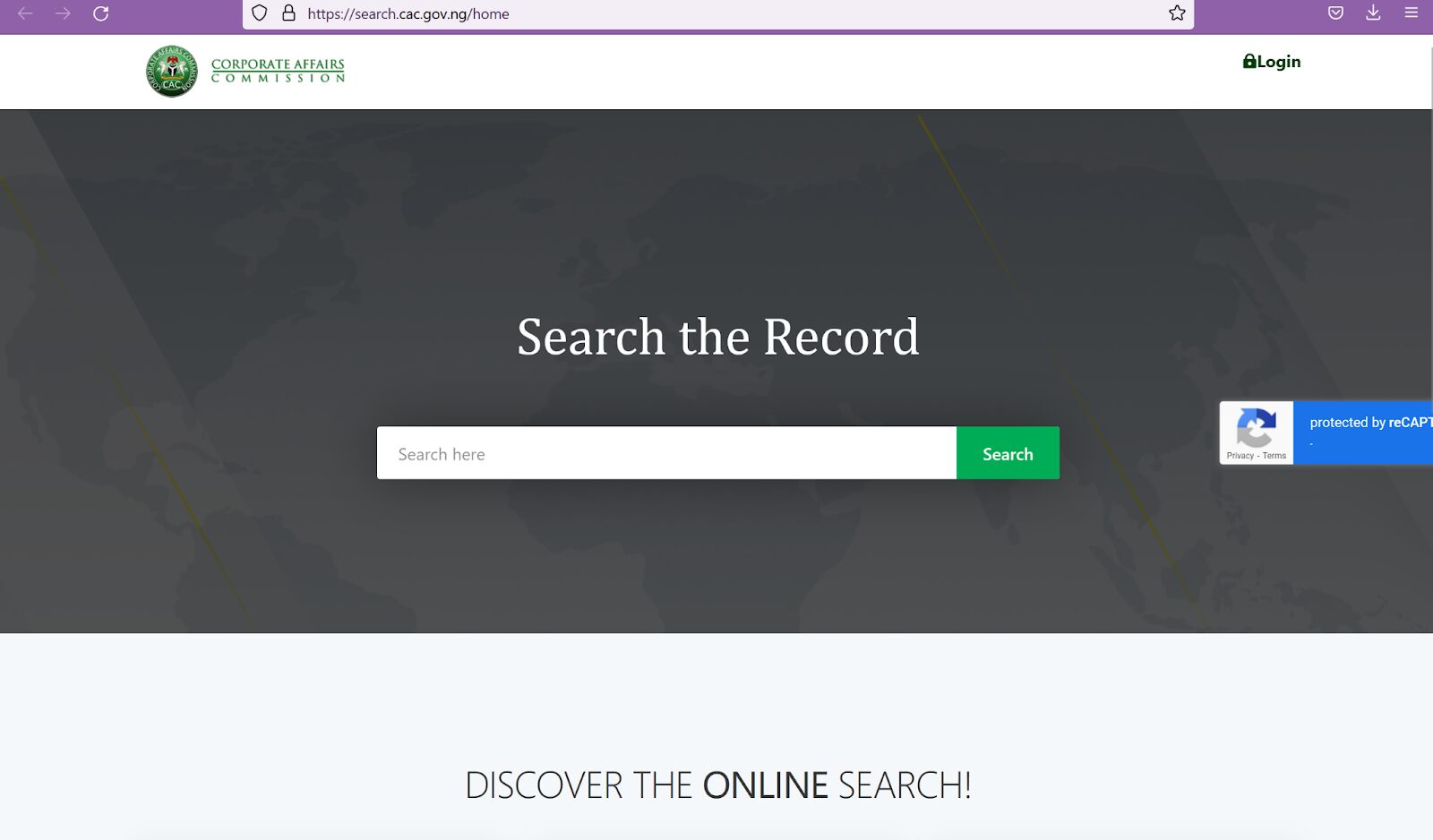
Pre-Registration Step 1: Conduct a public name search on the CAC portal.
The step entails the following:
- Propose two names for registration.
Carry out a public search of these three names by imputing these names on the search portal of the CAC.
Pre- Registration Step 2: Reserve a Name
This step entails the following:
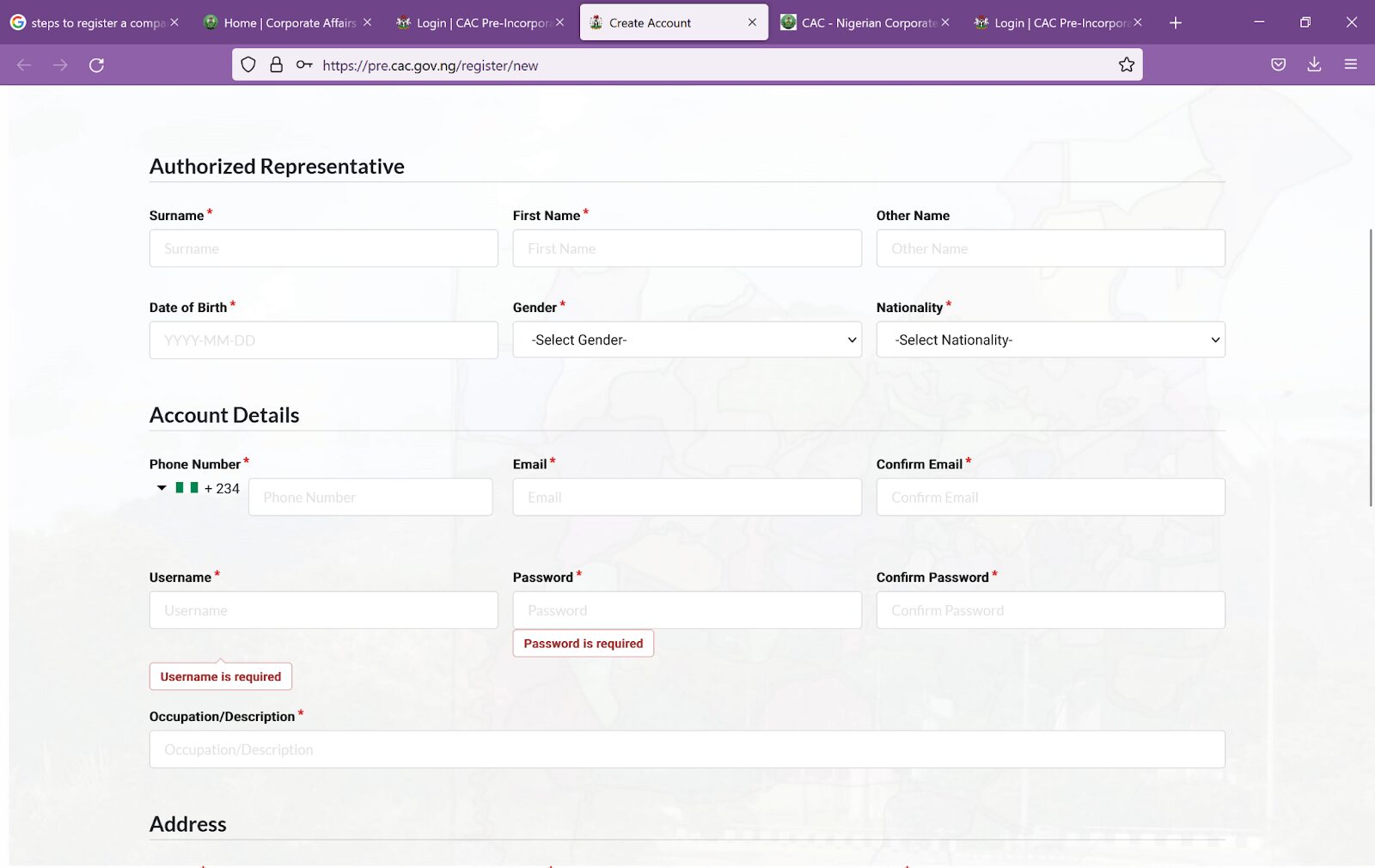
- Create an account on the CAC portal. This step is only followed if the business owner does not intend to use an accredited agent. An accredited agent is a lawyer or accountant or firm of lawyers or accountants recognised by the CAC to conduct affairs on behalf of corporate entities with the CAC.
- The CAC portal permits any member of the public to create an account on the portal but such person is deemed as a director of the company during the registration process. It is advised that an authorised representative or promoter of the company create this account.
- A name is reserved by submitting the two proposed names for the company on the CAC portal. It is done by selecting the appropriate options and providing the required information on the portal.
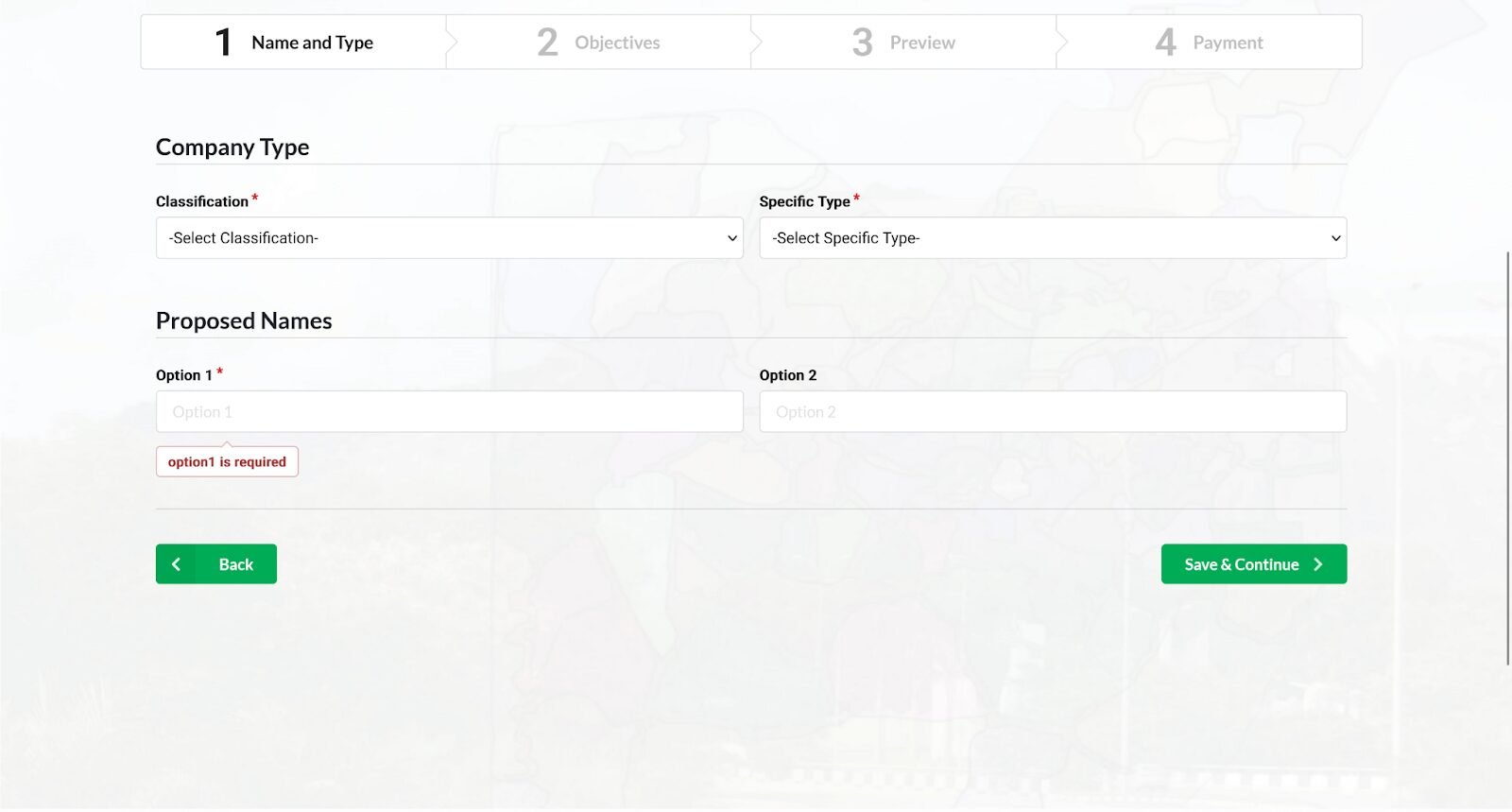
- This submission is accompanied by paying a fee of NGN 500 for Limited Liability Companies and NGN 5000 for Guarantee Companies.
- Where any of the proposed names are approved by the CAC, a name availability code will be issued.
- Where the name is rejected, the process is repeated again as well as the payment of the fee.
- A proposed name can be rejected for the following reasons:
- It is identical or in conflict to the name or trademark of a company or business name or partnership already in existence.
- Except it is a Guarantee Company, the proposed name must not contain the words “Chamber of Commerce”.
- The CAC believes that such a proposed name is capable of misleading on the nature of business being carried out.
- The CAC believed that the proposed name contains a word that is intended to mislead the public as to race, religion, tribe and nationality of the persons by whom the business is wholly or mainly owned or controlled.
- The CAC believes that the name would undermine public peace and national security.
Registration Steps:
These are the steps leading to the registration of a business as a company. Company registration begins after the CAC issues the name availability code. These steps are as follows:
Step 1:
After logging into the portal, click on new company registration. This would lead to a page asking that the name availability code be provided. 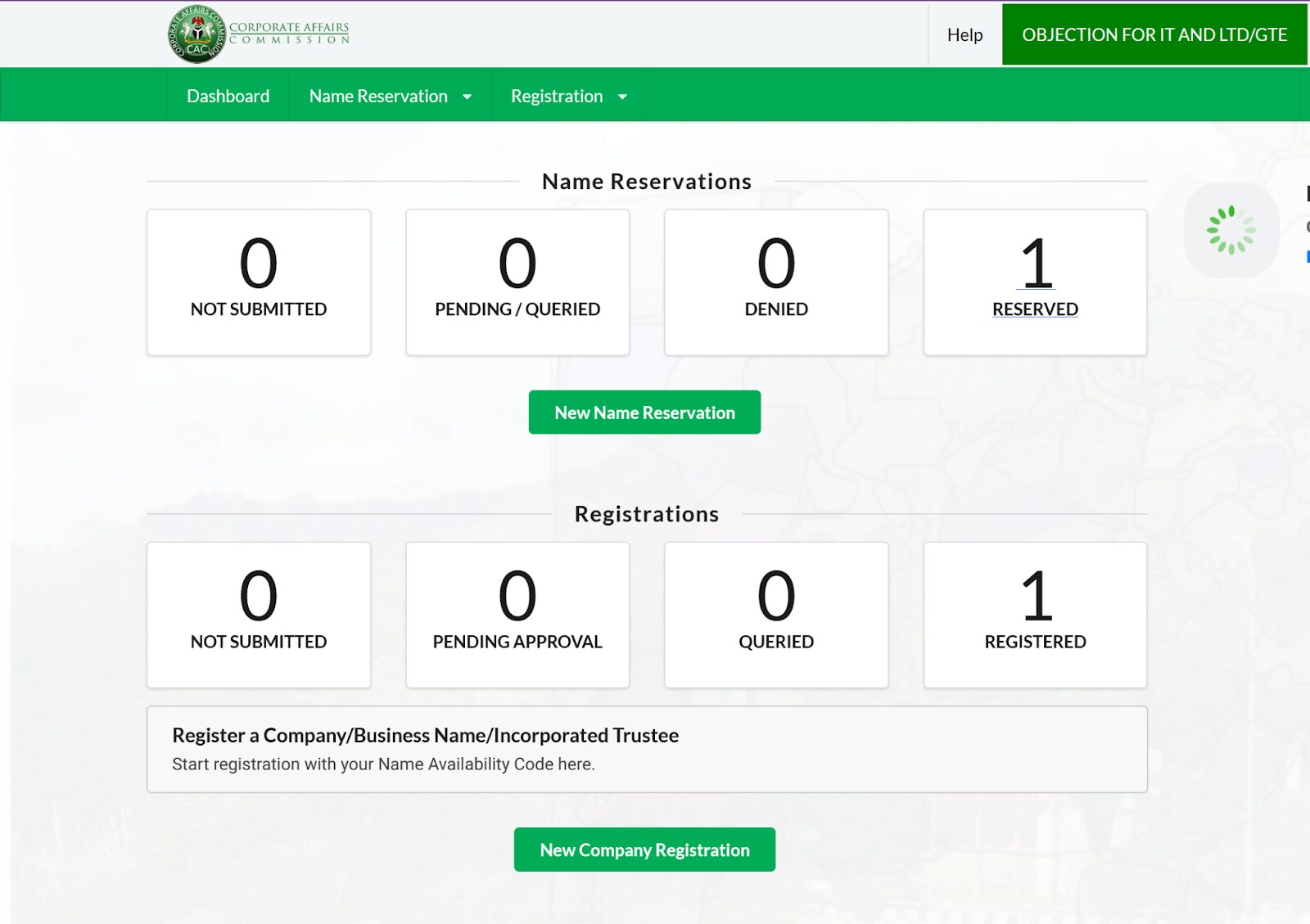
Step 2:
Input the name availability code on the page as provided by the CAC.
Step 3:
This would immediately lead to a page with Form CAC 1.1.
Step 4:
Complete this form by providing the requested information about the business. This information includes the following:
- Particulars of the Company; Approved name of the company, company type, principal business activity and registered office address.
- Memorandum and Articles of Association: A memorandum of association is a document signed by all the shareholders or guarantors agreeing to form a company. The articles of association is a document stating the rules which the company would be governed by. The business owner has the option of either adopting the model memorandum and articles of Association provided by the Companies and Allied Matters Act, 2020 or adopt them with amendments. This is done by selecting the desired option.
- Officers of the Company: The details of the proposed officers of the company should be provided. These details include that of the company secretary and directors. A small company has the option of providing the details of only one director as a secretary is not required. Other companies which are not small companies must provide details of at least two directors and a secretary. The details of the of the proposed officers of the company to be provided include; names, residential addresses and means of identification.
- Statement of Issued Share Capital: This is the amount of shares issued for subscription to the members of the Company. The details on the class of shares, numbers of shares and the particulars of members who subscribed for the shares are to be stated. For companies limited by guarantee, details of guarantors and the amount of money guaranteed is stated.
- If there is a company or person with significant control of the company, these details are to be stated on the form.
Step 5:
After completing this form, it will be submitted to the CAC via its portal. This submission is to be accompanied by the payment of the prescribed registration fee. The prescribed registration fee is dependent on the value of the company’s issued share capital.
- If the issued capital of the company is NGN1-million or less, the registration fee is NGN 10 000 for private companies and NGN 20 000 for public companies.
- If the issued capital is within NGN1-million to NGN 500-million, the registration fee is NGN5000 for every NGN1-million share capital or part thereof for private companies and NGN10 000 for public companies.
- If the issued capital is above NGN500-million, the registration fee is NGN7500 for every NGN1-million share capital for private companies and NGN15000 for public companies.
Step 6:
After the payment of the registration fee, the CAC would either approve and issue a certificate of registration to the company or issue queries on the information provided. The issued certification of registration is accompanied by certified true copies of the memorandum of association and the CAC form 1.1.
Post-Registration Steps:
This step includes compliance requirements expected from a company after it is registered. These steps are dependent on the transaction the company intends to carry out. They include:
- Change of Name
- Increase or Decrease in issued share capital
- Re-registration from a private company to a public company
- Notice of change in company’s financial year end
- Change in registered address of the company
- Change of directors; and
- Filing of annual returns.
However, the filing of annual returns is to be done annually by every company registered with the CAC. This is done by completing and submitting Form CAC 19 accompanied with the payment of NGN5000 for private companies and guarantee companies and NGN10000 for public companies.
Conclusion:
Registering your business as a company gives your business a legal identity and personality distinct from the business owner.
This legal identity enables the company to do the following:
- Sue and be sued;
- Pay the taxes levied to it by the relevant government authority;
- Enjoy the incentives provided to business by the government to encourage economic growth;
- Business expansion to other jurisdictions
- Take low interest business loans with finance institutions; and
- Open a bank account with banking institutions.
In conclusion registering a business as a company is less challenging if the steps highlighted above are followed.
However, it is important to point out that this article is only intended to serve as a guide and not to replace proper legal advice.
If you have further questions about registering a business as a company, book a free session with an expert.





