How to Review and Interpret a Business Contract

by Counseal Team
Updated June 2, 2025

Picture this scenario: You’ve just secured what appears to be the deal of a lifetime for your startup. The excitement is palpable, contracts are ready for signing, and success seems within reach. Yet before you put pen to paper, consider this sobering reality—thorough contract review isn’t merely recommended; it’s essential for your business survival.
- The Critical Importance of Contract Review for Nigerian Entrepreneurs
- Understanding Business Contracts: Foundations and Framework
- Why Contract Review Cannot Be Optional
- Systematic Approach to Contract Review
- Tools and Techniques for Effective Review
- Avoiding Common Contract Review Pitfalls
- Best Practices for Contract Interpretation
- Strategic Contract Negotiation Insights
- Implementation and Follow-Through
- Conclusion: Mastering Contract Review for Business Success
The Critical Importance of Contract Review for Nigerian Entrepreneurs
Picture this scenario: You’ve just secured what appears to be the deal of a lifetime for your startup. The excitement is palpable, contracts are ready for signing, and success seems within reach. Yet before you put pen to paper, consider this sobering reality—thorough contract review isn’t merely recommended; it’s essential for your business survival.
A business contract represents far more than legal documentation; it forms the foundation of your commercial relationships and defines the parameters within which your business operates. For Nigerian entrepreneurs navigating an increasingly complex regulatory landscape, contract review serves as your first line of defence against costly disputes, regulatory violations, and partnership failures.
The stakes couldn’t be higher. According to recent data from the Lagos Chamber of Commerce, over 60% of business disputes in Nigeria stem from poorly understood or inadequately reviewed contractual agreements. These disputes don’t just drain financial resources—they divert crucial time and energy from core business activities, often proving fatal for emerging enterprises.
What This Comprehensive Guide Delivers
This article provides Nigerian entrepreneurs with a systematic approach to contract review and interpretation. You’ll discover practical methodologies for analysing complex legal documents, learn to identify potentially problematic clauses before they become costly mistakes, and develop the confidence to negotiate terms that protect your interests.
We’ll examine real-world examples from the Nigerian business environment, provide step-by-step tutorials for effective review processes, and share insights that can prevent the contractual pitfalls that have derailed countless promising ventures. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your first startup, this guide equips you with essential skills for navigating Nigeria’s commercial legal landscape.
About the Author’s Expertise
Dele Omotosho brings over six years of hands-on experience building and scaling startups across Nigeria’s dynamic business ecosystem. As founder of counseal.com, he has witnessed firsthand how contractual oversights can make or break entrepreneurial ventures. His experience spans local startups to multinational partnerships, providing him with unique insights into both domestic and international contracting practices.
Through counseal.com, Dele has helped numerous Nigerian businesses navigate complex legal agreements, from early-stage partnership deals to sophisticated international investment contracts. His practical approach combines legal acumen with entrepreneurial understanding, making complex contractual concepts accessible to business owners at every stage of their journey.
Understanding Business Contracts: Foundations and Framework
A business contract functions as the legal architecture governing commercial relationships between parties. Think of it as the comprehensive rulebook that establishes expectations, obligations, and remedies should disagreements arise. Unlike informal agreements or verbal understandings, business contracts create legally enforceable obligations that courts will uphold.
Essential Components of Valid Business Contracts
Every enforceable business contract must contain five fundamental elements:
Offer and Acceptance: One party must make a clear, specific offer, and another party must accept that offer without material modifications. This creates the basic agreement framework.
Consideration: Each party must provide something of value—whether money, services, goods, or promises. This exchange of value distinguishes contracts from mere gifts or one-sided promises.
Mutual Consent: All parties must fully understand and voluntarily agree to the contract terms. This requires clear communication and absence of fraud, duress, or undue influence.
Legal Purpose: The contract’s objective must be lawful. Agreements involving illegal activities cannot be enforced through legal channels.
Competent Parties: All contracting parties must possess legal capacity—they must be of legal age, mentally competent, and legally authorised to enter agreements.
Understanding these components helps entrepreneurs identify when agreements might be legally vulnerable or unenforceable.
Common Business Contract Types in Nigeria
Nigerian entrepreneurs regularly encounter several contract categories:
Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs): Protect confidential information during business discussions, partnerships, or employment relationships. These prove particularly crucial in Nigeria’s competitive technology and manufacturing sectors.
Employment Contracts: Define relationships with staff members, establishing duties, compensation, benefits, and termination procedures whilst ensuring compliance with Nigerian labour laws.
Sales and Service Agreements: Govern transactions involving goods or services, specifying delivery terms, payment schedules, quality standards, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Partnership Agreements: Structure business relationships between co-founders or business partners, detailing profit-sharing, decision-making authority, and exit procedures.
Lease Agreements: Cover property rentals for business premises, outlining rental terms, maintenance responsibilities, and renewal options—particularly important given Nigeria’s complex property laws.
Supply and Distribution Agreements: Manage relationships with suppliers or distributors, establishing delivery schedules, pricing mechanisms, and performance standards.
Why Contract Review Cannot Be Optional
Legal Implications: Protecting Your Business Foundation
Contract review serves as your business’s legal immune system, identifying potential threats before they materialise into costly problems. Nigerian commercial law provides limited protection for parties who fail to understand their contractual obligations, placing responsibility squarely on business owners to comprehend what they’re signing.
Consider the legal principle of caveat emptor—let the buyer beware. Nigerian courts generally hold that sophisticated business parties should understand their contractual commitments. This means claiming ignorance of contract terms rarely provides legal relief once disputes arise.
Legal implications extend beyond immediate contractual relationships. Poorly reviewed contracts can create:
- Regulatory compliance violations resulting in government penalties
- Intellectual property disputes that threaten core business assets
- Employment law violations exposing businesses to labour disputes
- Tax implications affecting ongoing financial obligations
Financial Risks: The True Cost of Contractual Oversights
Financial consequences of inadequate contract review extend far beyond obvious penalties or dispute resolution costs. Hidden financial risks include:
Cash Flow Disruption: Unfavourable payment terms can strangle business operations. A contract requiring 90-day payment cycles instead of 30-day terms can create devastating cash flow challenges for small businesses.
Unexpected Cost Escalations: Automatic renewal clauses, price adjustment mechanisms, or hidden fee structures can dramatically increase operational expenses without warning.
Liability Exposure: Inadequate indemnification clauses can expose businesses to unlimited liability for third-party claims, potentially bankrupting otherwise successful ventures.
Opportunity Costs: Restrictive non-compete or exclusivity clauses can prevent businesses from pursuing profitable opportunities, limiting growth potential.
Get Expert Guidance on Your Nigerian Business Journey
Join 1000+ entrepreneurs who’ve transformed their Nigerian business plans with our strategic guidance. In one focused session, unlock:
- Market-ready opportunity assessment
- Regulatory compliance roadmap
- Implementation strategy tailored to your business
- Cost framework and resource planning
What You’ll Receive:
- Personalized Strategy Session with a Nigerian market specialist
- Custom Implementation Roadmap based on your specific business goals
- Regulatory Checklist tailored to your industry
- Priority Access to our implementation team when you’re ready
How It Works:
- Select your preferred time slot below
- Complete a brief business assessment
- Join your private Zoom session
- Receive your actionable implementation plan
Limited availability — Only 8 sessions offered each week
Systematic Approach to Contract Review
Phase One: Initial Reading and Overview
Strategic Skimming for Key Information
Begin contract review with strategic skimming to understand the document’s structure and identify critical sections requiring detailed analysis. This approach prevents getting lost in complex legal language whilst ensuring comprehensive coverage.
Start by examining the contract’s table of contents or section headings. Most well-drafted business contracts follow logical organisation patterns: parties identification, definitions, primary obligations, payment terms, performance standards, termination procedures, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Focus initially on these high-priority elements:
- Party identification and legal standing
- Contract duration and renewal mechanisms
- Primary obligations and deliverables
- Payment terms and financial obligations
- Termination and exit procedures
- Dispute resolution requirements
Look for defined terms, typically found in early contract sections or footnotes. These definitions often dramatically alter standard word meanings, making their understanding crucial for accurate interpretation.
Identifying All Contracting Parties
Determine exactly who you’re contracting with—this seemingly simple step often reveals significant complications. Contracts might involve:
- Individual proprietors with personal liability exposure
- Registered companies with limited liability protection
- Subsidiaries of larger corporations with potential parent company guarantees
- Foreign entities subject to different legal jurisdictions
Verify contracting parties’ legal status through Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC) searches. Ensure the individual signing has proper authority to bind the organisation—unauthorised signatures can void entire agreements.
For foreign entities, understand which country’s laws govern the relationship and whether Nigerian courts have jurisdiction over disputes.
Phase Two: Detailed Clause-by-Clause Analysis
Payment Terms: The Financial Foundation
Payment terms directly impact cash flow and business sustainability. Analyse these critical components:
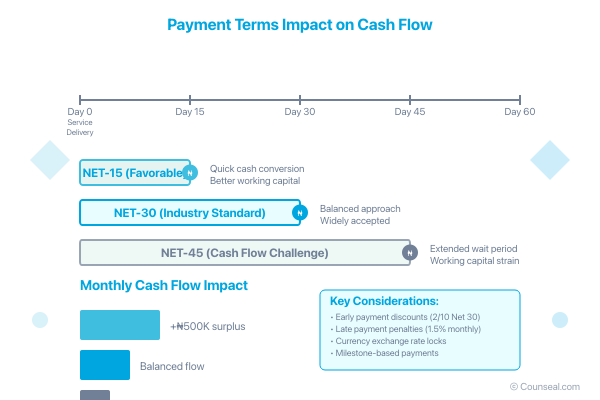
Payment Schedules: Examine when payments are due relative to service delivery or product shipment. Net-30 terms (payment due 30 days after invoice) are standard for many industries, whilst Net-15 or Net-45 terms might be negotiable based on relationship dynamics.
Payment Methods: Understand required payment mechanisms—bank transfers, cheques, or electronic payments. International contracts may require specific currencies or banking procedures.
Late Payment Consequences: Identify penalties for delayed payments, including interest rates and potential service suspension rights. Nigerian contract law generally permits reasonable late payment charges.
Early Payment Incentives: Some contracts offer discounts for accelerated payment, improving cash flow for both parties.
Currency and Exchange Rate Provisions: For international contracts, determine currency requirements and exchange rate calculation methods, particularly important given naira volatility.
Delivery and Performance Schedules
Performance schedules establish expectations and provide remedies for delays or failures. Examine:
Milestone Definitions: Understand specific deliverables and completion criteria. Vague performance standards create dispute opportunities.
Timeline Flexibility: Look for force majeure clauses addressing unforeseeable circumstances like government policy changes, natural disasters, or supply chain disruptions—particularly relevant in Nigeria’s dynamic regulatory environment.
Performance Penalties: Identify consequences for missed deadlines, including financial penalties, contract termination rights, or service level credits.
Acceptance Procedures: Understand how deliverables are reviewed and approved, including rejection rights and correction processes.
Favourable vs. UnFavourable Term Examples
Favourable Terms Include:
- Clear performance metrics with reasonable timelines
- Balanced liability allocation between parties
- Flexible termination clauses protecting business interests
- Reasonable payment terms supporting cash flow management
- Comprehensive intellectual property protections
Unfavourable Terms to Avoid:
- Automatic renewal clauses without clear opt-out procedures
- Disproportionate penalty structures for minor breaches
- Unlimited liability exposure for consequential damages
- Restrictive non-compete clauses limiting future business opportunities
- Ambiguous performance standards creating dispute potential
Phase Three: Legal Clause Examination
Indemnification Clauses: Your Legal Shield
Indemnification clauses determine who bears responsibility for third-party claims arising from contract performance. These provisions can protect your business from devastating liability exposure or create unexpected financial obligations.
Mutual Indemnification: Both parties protect each other from claims arising from their respective actions. This balanced approach typically provides fair risk allocation.
One-Way Indemnification: Only one party provides protection, potentially creating unbalanced risk exposure. Carefully evaluate whether such arrangements are justified by underlying business dynamics.
Scope Limitations: Some indemnification clauses exclude certain claim types (intellectual property disputes, regulatory violations, or gross negligence). Understand these limitations and their business implications.
Nigerian courts generally enforce reasonable indemnification provisions, making careful drafting essential for effective protection.
Termination Clauses: Planning Your Exit Strategy
Termination clauses provide escape routes when business relationships deteriorate or circumstances change. Analyse these components:
Termination for Cause: Allows contract termination when the other party materially breaches agreement terms. Ensure “material breach” is clearly defined and includes specific examples.
Termination for Convenience: Permits contract termination without specific cause, typically requiring advance notice and potential penalty payments. This flexibility can be valuable as business needs evolve.
Notice Requirements: Understand required notification periods and procedures. Inadequate notice can create liability exposure even when termination is otherwise justified.
Post-Termination Obligations: Examine ongoing responsibilities after contract termination, including confidentiality requirements, return of materials, or non-compete restrictions.
Ensuring Nigerian Legal Compliance
Understanding Local Regulatory Requirements
Nigerian businesses must navigate complex regulatory frameworks spanning multiple agencies and jurisdictions. Key compliance areas include:
Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC) Requirements: Ensure contracting entities are properly registered and maintain good standing with corporate regulators.
Federal Inland Revenue Service (FIRS) Obligations: Understand tax implications of contractual arrangements, including withholding tax requirements and VAT obligations.
Industry-Specific Regulations: Different sectors face unique regulatory requirements:
- Technology companies must comply with Nigeria Data Protection Regulation (NDPR)
- Financial services firms operate under Central Bank of Nigeria oversight
- Manufacturing businesses must meet National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control (NAFDAC) standards
- Import/export operations require Nigeria Customs Service compliance
Technology Sector Compliance Checklist
For technology startups and digital businesses, ensure contracts address:
✓ Data Protection Compliance: Implement NDPR requirements for personal data collection, processing, and storage ✓ Intellectual Property Registration: Protect trademarks, copyrights, and patents through appropriate Nigerian agencies
✓ Employment Law Compliance: Structure employment contracts according to Nigerian Labour Act requirements ✓ Foreign Exchange Regulations: Comply with Central Bank foreign currency transaction requirements ✓ Tax Registration and Filing: Maintain current FIRS registration and meet filing deadlines
Tools and Techniques for Effective Review
Manual Review Methodologies
The Systematic Checklist Approach
Develop standardised checklists to ensure consistent, thorough contract review. A comprehensive checklist should include:
Pre-Review Setup:
- Verify all parties’ legal status and authority
- Confirm contract version and amendment history
- Gather relevant background documentation
- Set aside adequate review time without interruptions
Content Review Elements:
- Primary obligations and deliverables
- Payment terms and financial obligations
- Performance timelines and milestones
- Termination and renewal procedures
- Liability and indemnification terms
- Dispute resolution mechanisms
- Governing law and jurisdiction clauses
Post-Review Actions:
- Document questions and concerns for negotiation
- Identify required legal or financial consultation
- Create implementation timeline and responsibility assignments
Redlining and Collaborative Review
Redlining—the process of marking proposed changes directly on contract documents—facilitates effective negotiation and ensures all parties understand proposed modifications.
Effective Redlining Process:
- Use Professional Software: Microsoft Word’s “Track Changes” or Google Docs’ “Suggestion Mode” provide robust redlining capabilities with clear change documentation.
- Categorise Changes: Use different colours or comment types for different change categories—legal concerns, business terms, or clarification requests.
- Provide Clear Explanations: Each suggested change should include explanatory comments describing the reasoning and desired outcome.
- Maintain Version Control: Create clear version numbering systems to track negotiation progress and prevent confusion.
- Document Rationale: Maintain separate notes explaining negotiation strategy and fallback positions for complex terms.
Technology-Enhanced Review Tools
AI-Powered Contract Analysis
Artificial intelligence tools are revolutionising contract review by providing rapid initial analysis and risk identification. Leading AI contract review platforms can:
Identify Risk Patterns: Analyse thousands of contract clauses to identify potentially problematic terms or unusual provisions requiring attention.
Benchmark Against Standards: Compare contract terms against industry standards and best practices, highlighting deviations requiring evaluation.
Extract Key Information: Automatically compile critical contract data including dates, financial terms, and performance obligations.
Generate Review Reports: Provide comprehensive summaries highlighting high-risk areas and recommended focus points for human review.
Benefits and Limitations of AI Review Tools
AI Tool Advantages:
- Dramatically reduced review time for initial analysis
- Consistent identification of common risk patterns
- Cost-effective screening for routine contract types
- Objective analysis free from human fatigue or oversight
AI Tool Limitations:
- Cannot replace human judgement for complex business decisions
- May miss context-specific risks or opportunities
- Requires ongoing training for Nigerian legal requirements
- Limited effectiveness for highly specialised or novel contract types
For Nigerian entrepreneurs, AI tools work best as initial screening mechanisms, followed by thorough human review focusing on business-specific considerations and local legal requirements.
Avoiding Common Contract Review Pitfalls
The Devil in the Details: Why Small Print Matters
Many entrepreneurs focus exclusively on headline terms—price, delivery dates, and primary obligations—whilst overlooking seemingly minor provisions that can create major problems. Consider these easily missed but potentially costly details:
Automatic Renewal Clauses: A software licensing agreement might automatically renew for additional one-year terms unless cancelled with 90-day advance notice. Missing this deadline could lock your business into unwanted commitments.
Interest and Penalty Calculations: Late payment clauses might compound daily rather than monthly, dramatically increasing costs for delayed payments.
Notice Requirements: Contracts often specify exact procedures for providing notices—registered mail, email confirmation, or in-person delivery. Failure to follow procedures precisely can invalidate otherwise valid notices.
Definition Ambiguities: Terms like “material breach” or “reasonable efforts” might seem clear but can create interpretation disputes without precise definitions.
Case Example: The Compound Interest Surprise
FastLogistics, a Lagos-based delivery company, signed a vehicle leasing agreement focusing primarily on monthly payment amounts and lease duration. However, they overlooked a clause specifying that late payments would accrue interest at 2% monthly, compounded daily.
When cash flow challenges caused FastLogistics to make payments 15 days late for three consecutive months, they discovered they owed an additional ₦180,000 in interest charges—far exceeding their budgeted late payment assumptions. The compounding calculation meant their effective late payment penalty was nearly 27% annually, creating a debt spiral that forced business restructuring.
A careful review of the interest calculation methodology could have prompted renegotiation or alternative financing arrangements, preventing this financial crisis.
Decoding Legal Jargon: Essential Term Translations
Legal language often obscures rather than clarifies meaning, making translation into plain English essential for proper understanding.
Critical Legal Terms Simplified
Force Majeure: “Superior force” referring to unforeseeable circumstances that prevent contract performance—natural disasters, government actions, or other extraordinary events beyond party control.
Liquidated Damages: Pre-agreed compensation amounts for specific contract breaches, eliminating the need to prove actual damages in court.
Indemnification: One party’s promise to protect another from specified losses or claims, essentially providing insurance against certain risks.
Severability: If one contract provision is deemed invalid or unenforceable, the remaining provisions continue in effect rather than voiding the entire agreement.
Jurisdiction and Governing Law: Determines which courts can hear disputes and which country’s or state’s laws will be applied to interpret contract terms.
Representations and Warranties: Statements of fact about current conditions (representations) and promises that certain conditions will continue (warranties), with breach providing grounds for contract termination or damage claims.
Legal Jargon Translation Strategy
Step 1: Identify Unfamiliar Terms: Highlight any legal terms or phrases that seem unclear or unusually complex.
Step 2: Research Definitions: Use legal dictionaries, online resources, or legal consultation to understand precise meanings.
Step 3: Consider Business Context: Understand how legal terms apply to your specific business situation and industry.
Step 4: Seek Professional Clarification: When terms remain unclear or seem particularly important, consult qualified legal counsel for explanation.
Step 5: Document Understanding: Create a glossary of key terms for future reference and team education.
Best Practices for Contract Interpretation
Understanding Contextual Framework
Effective contract interpretation requires understanding the broader business and legal context surrounding the agreement. Nigerian contract law emphasises objective interpretation—what reasonable parties would understand the contract to mean given the circumstances.
Industry Context Considerations
Different industries have established customs and practices that influence contract interpretation:
Technology Sector: Software licensing agreements typically include implied warranties about functionality and support, even when not explicitly stated. However, limitation of liability clauses are generally more restrictive than in other industries.
Manufacturing: Quality standards often reference industry specifications (ISO standards, NAFDAC requirements) even when not fully detailed in contracts. Delivery terms carry greater weight due to production scheduling implications.
Professional Services: “Best efforts” obligations are typically interpreted more strictly than in product-based industries, with higher expectations for expertise and care.
Real Estate: Local customs regarding property conditions, maintenance responsibilities, and transfer procedures significantly influence contract interpretation.
Regulatory Environment Impact
Nigerian regulatory requirements create interpretive context that may override contract terms:
Consumer Protection: Contracts with individual consumers cannot waive certain statutory rights, regardless of contract language.
Employment Law: Labour contracts must comply with minimum wage, working time, and termination requirements established by Nigerian law.
Foreign Exchange: International contracts must consider Central Bank of Nigeria foreign currency regulations that may limit certain provisions.
When Professional Legal Consultation Becomes Essential
Clear Indicators for Legal Consultation
Certain contract characteristics signal the need for professional legal review:
High Financial Stakes: Contracts involving significant financial commitments—typically exceeding 10% of annual revenue—warrant professional review regardless of apparent simplicity.
Complex Liability Allocation: Indemnification clauses, limitation of liability provisions, or insurance requirements create potential exposure requiring expert evaluation.
International Elements: Cross-border contracts involve multiple legal systems, currency considerations, and enforcement challenges requiring specialised expertise.
Intellectual Property Components: Licensing, development, or transfer of intellectual property rights involves complex legal principles with long-term business implications.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements: Contracts in heavily regulated industries (financial services, telecommunications, healthcare) require compliance verification.
Novel Business Arrangements: Innovative business models or partnership structures may lack established legal precedents, requiring creative legal structuring.
Maximising Legal Consultation Value
Prepare Comprehensive Background: Provide lawyers with complete business context, including strategic objectives, risk tolerance, and industry considerations.
Focus on Business Objectives: Frame legal consultation around business goals rather than legal technicalities, ensuring advice supports commercial success.
Request Plain English Explanations: Insist that legal counsel explain complex concepts in business terms, ensuring you understand implications and alternatives.
Discuss Implementation Practicalities: Address how contract terms will work in day-to-day business operations, identifying potential practical challenges.
Plan for Future Modifications: Understand procedures for contract amendments, renewal negotiations, or termination processes.
Strategic Contract Negotiation Insights
Leveraging Review Findings for Better Terms
Thorough contract review often reveals negotiation opportunities that can significantly improve business outcomes. Transform review findings into negotiation advantages:
Benchmarking Against Standards: When contract terms deviate significantly from industry norms, use this information to negotiate more favourable provisions.
Risk Reallocation: Identify clauses that create disproportionate risk exposure and propose more balanced alternatives.
Performance Incentives: Suggest bonus structures or penalty reductions that align with realistic performance capabilities.
Flexibility Enhancements: Negotiate termination clauses, modification procedures, or renewal options that provide business agility.
Building Long-Term Relationship Value
Contract review should consider not just immediate legal protection but also long-term relationship dynamics:
Mutual Benefit Focus: Propose terms that create value for both parties, encouraging collaboration rather than adversarial enforcement.
Clear Communication Mechanisms: Establish regular review meetings, performance discussions, and issue resolution procedures.
Growth Accommodation: Include provisions that adapt to changing business needs, market conditions, or regulatory requirements.
Dispute Prevention: Create early warning systems and collaborative problem-solving mechanisms to prevent minor issues from becoming major disputes.
Implementation and Follow-Through
Creating Contract Management Systems
Effective contract review extends beyond initial analysis to ongoing management and monitoring:
Centralised Contract Storage: Implement secure, searchable systems for storing all business contracts with version control and access management.
Performance Tracking: Create mechanisms to monitor compliance with contract obligations, including deadline tracking and deliverable verification.
Renewal Management: Establish calendars and alert systems for contract renewals, termination deadlines, and renegotiation opportunities.
Amendment Documentation: Maintain clear records of all contract modifications, including rationale and approval processes.
Team Education and Capacity Building
Contract review effectiveness improves when entire teams understand contractual obligations and requirements:
Key Personnel Training: Ensure relevant staff understand contract terms affecting their responsibilities and decision-making authority.
Escalation Procedures: Create clear processes for addressing contract disputes, performance issues, or modification requests.
Regular Review Meetings: Schedule periodic contract performance discussions to identify emerging issues and improvement opportunities.
Documentation Standards: Establish consistent approaches to contract-related communications and record-keeping.
Conclusion: Mastering Contract Review for Business Success
Contract review represents one of the most critical skills Nigerian entrepreneurs must develop to navigate today’s complex business environment successfully. The investment in thorough contract analysis—whether through personal skill development, professional consultation, or technology-enhanced tools—consistently delivers returns that far exceed its costs.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the systematic approaches that transform contract review from a necessary burden into a strategic business advantage. From understanding fundamental legal components to leveraging AI-powered analysis tools, from avoiding common pitfalls to negotiating favourable terms, effective contract review provides the foundation for sustainable business growth.
The Nigerian business landscape continues evolving rapidly, with new regulations, market dynamics, and international opportunities creating both challenges and possibilities. Entrepreneurs who master contract review and interpretation position themselves to capitalise on opportunities whilst protecting against risks that have derailed countless promising ventures.
Key Takeaways for Immediate Implementation
Develop Systematic Review Processes: Implement standardised checklists and procedures that ensure consistent, thorough contract analysis across all business agreements.
Invest in Professional Relationships: Build relationships with qualified legal counsel who understand your industry and business model, enabling rapid consultation when complex issues arise.
Leverage Technology Appropriately: Use AI-powered tools for initial contract screening whilst maintaining human oversight for business-critical decisions and industry-specific considerations.
Focus on Business Objectives: Always interpret contract terms within the context of your broader business strategy, ensuring agreements support rather than hinder commercial success.
Plan for Change: Structure contracts with flexibility mechanisms that accommodate business growth, market evolution, and regulatory changes.
Final Thoughts from Dele Omotosho
After six years of building startups and working with entrepreneurs across Nigeria’s dynamic business ecosystem, I’ve witnessed how contract review mastery separates successful enterprises from those that struggle or fail. The entrepreneurs who thrive understand that contracts are not merely legal necessities—they are strategic tools that enable business success.
Every contract you review and negotiate effectively strengthens your business foundation. Every clause you understand and optimise contributes to your competitive advantage. Every risk you identify and mitigate protects your entrepreneurial dreams from preventable threats.
The path to contract review mastery requires dedication, continuous learning, and sometimes professional guidance. However, the investment pays dividends throughout your entrepreneurial journey, providing confidence, protection, and strategic advantage in every business relationship you forge.
Remember that contract review is not about creating perfect documents—it’s about understanding your commitments, protecting your interests, and building business relationships that support mutual success. With the knowledge and tools provided in this guide, you’re equipped to approach every contract with confidence and strategic insight.
Now go forth and build the successful, legally protected business you envision. Your future self will thank you for the careful attention you give to every contract you sign today.Transform your contract review capabilities with professional guidance. Ready to protect your business interests whilst pursuing growth opportunities? Visit counseal.com/start to schedule your strategic consultation and take the first step toward comprehensive legal protection for your entrepreneurial journey.





