Tax Implications for Nigerian Entrepreneurs Running a Business from Abroad

by Counseal Team
Updated May 30, 2025

Running a business across international borders presents unique challenges, particularly when it comes to taxation. For Nigerian entrepreneurs operating from abroad, understanding these implications is crucial for both compliance and profitability.
- Navigating Tax Implications for Nigerian Entrepreneurs Abroad
- Why Tax Implications Matter
- Understanding Tax Residency
- Tax Obligations for Nigerian Entrepreneurs Abroad
- Registering a Foreign Company in Nigeria
- Filing Tax Returns: Tutorial for Non-Resident Companies
- Expert Insights
- Summary of Key Points
Navigating Tax Implications for Nigerian Entrepreneurs Abroad
Running a business across international borders presents unique challenges, particularly when it comes to taxation. For Nigerian entrepreneurs operating from abroad, understanding these implications is crucial for both compliance and profitability.
Why Tax Implications Matter
Managing international tax obligations isn’t merely about compliance—it’s fundamental to your business’s sustainability and growth. Consider this scenario: You’re managing your thriving business from London when an unexpected tax notice arrives from Nigeria. Understanding your tax obligations beforehand can help you avoid such surprises and maintain smooth operations.
Understanding Tax Residency
Definition of Tax Residency
Tax residency determines where you’re obligated to pay taxes. It’s not simply about your physical location; it encompasses your significant economic and personal ties. For businesses, it often relates to incorporation location and management base.
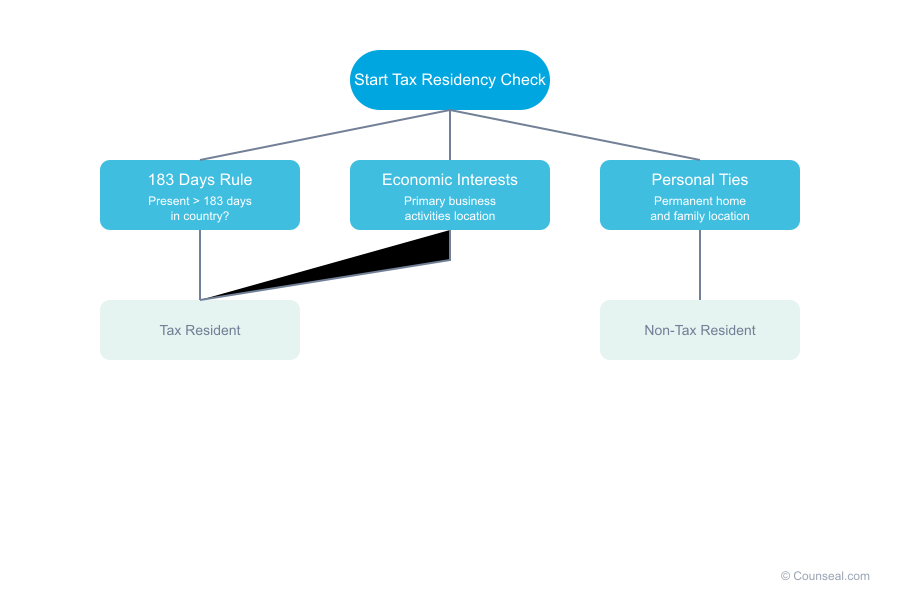
Criteria for Determining Tax Residency
For Individuals:
- The 183-day rule: Spending more than 183 days in a country typically establishes tax residency
- Economic interests: Where your primary business activities occur
- Personal ties: Location of permanent home and family
For Businesses:
- Place of incorporation
- Central management and control location
- Permanent establishment considerations
Companies Income Tax Act (CITA)
CITA serves as the foundation for corporate taxation in Nigeria. For entrepreneurs operating from abroad, understanding its provisions is essential.
Key Provisions Affecting Non-Resident Companies
- Tax obligations for Nigeria-sourced income
- Filing requirements and deadlines
- Permanent establishment implications
- Transfer pricing considerations
Finance Act, 2020
Recent amendments have introduced significant changes affecting international businesses:
- Revised definition of Significant Economic Presence (SEP)
- Digital transaction taxation
- Modified compliance requirements
- Updated filing obligations
Personal Income Tax Act (PITA)
PITA governs individual taxation, including entrepreneurs operating internationally. Key considerations include:
- Worldwide income reporting requirements
- Tax residency implications
- Digital service provisions
- Personal income documentation
Tax Obligations for Nigerian Entrepreneurs Abroad
Corporate Tax Obligations
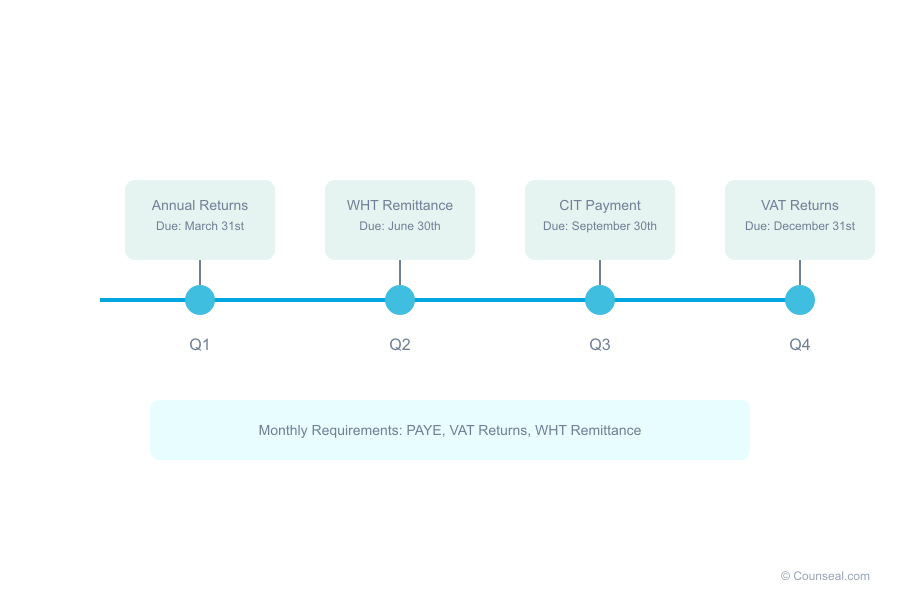
Filing Requirements for Non-Resident Companies
Non-resident companies earning income from Nigeria must:
- File annual tax returns
- Maintain proper documentation
- Report significant transactions
- Comply with digital economy regulations
Withholding Tax Obligations
- Standard 10% rate for most transactions
- Variations based on transaction type
- Treaty considerations
- Filing and payment schedules
Personal Tax Obligations
Nigerian individuals earning abroad must consider:
- Worldwide income declaration
- Double taxation agreements
- Foreign income exclusions
- Proper documentation requirements
Registering a Foreign Company in Nigeria
Step-by-Step Guide
- Company Name Reservation
- CAC portal registration
- Name availability check
- Reservation confirmation
- Documentation Preparation
- Memorandum and Articles of Association
- Share capital statement
- Director identification documents
- Application Submission
- Digital portal filing
- Document verification
- Processing requirements
- Certificate Acquisition
- Final approval process
- Documentation collection
- Registration completion
Filing Tax Returns: Tutorial for Non-Resident Companies
Understanding Your Tax Obligations
Non-resident companies must comply with:
- Company Income Tax (CIT)
- Value Added Tax (VAT)
- Digital service taxes
- Withholding tax requirements
Step-by-Step Filing Process
- FIRS Registration
- TIN acquisition
- Portal access setup
- Documentation requirements
- Financial Statement Preparation
- Profit and loss statements
- Balance sheets
- Supporting documentation
- Return Submission
- Online filing procedures
- Payment processes
- Compliance verification
Expert Insights
Future Trends in International Taxation
- Digital Economy Taxation
- OECD guidelines implementation
- Digital presence regulations
- Cross-border transaction requirements
- Environmental Considerations
- Sustainability incentives
- Carbon taxation
- Green business benefits
- Transparency Requirements
- Information exchange protocols
- Reporting standards
- Compliance documentation
Summary of Key Points
- Maintain accurate financial records
- Understand residency implications
- Comply with filing requirements
- Seek professional guidance
- Monitor regulatory changes
This guide reflects current regulations as of February 2025. For specific advice tailored to your business situation, consult with qualified tax professionals.





