Licensing and Commercialising Your Intellectual Property: A Strategic Guide for Nigerian Entrepreneurs

by Counseal Team
Updated June 2, 2025

If you’re building a business in Nigeria’s dynamic economy, understanding intellectual property is crucial for your success. Intellectual property represents the unique creations of your mind—your inventions, designs, brand names, artistic works, and proprietary processes. These intangible assets often provide the competitive edge that distinguishes your business in the marketplace.
- What is Intellectual Property (IP)?
- Types of Intellectual Property
- Why Protecting IP is Crucial for Nigerian Businesses
- Understanding IP Licensing
- Why Licensing and Commercialisation Matter for Business Growth
- Strategic Approaches to IP Commercialisation
- Essential Elements of Licensing Agreements
- Regulatory Landscape for Nigerian Businesses
- Common Challenges and Best Practices
- Financial Valuation and Analysis
- Case Studies: Nigerian IP Success Stories
- Strategic Implementation Framework
- Looking Forward: The Future of IP in Nigeria
- Conclusion
What is Intellectual Property (IP)?
If you’re building a business in Nigeria’s dynamic economy, understanding intellectual property is crucial for your success. Intellectual property represents the unique creations of your mind—your inventions, designs, brand names, artistic works, and proprietary processes. These intangible assets often provide the competitive edge that distinguishes your business in the marketplace.
IP encompasses the innovations that drive economic growth. From the algorithms powering fintech solutions to the distinctive branding of consumer products, intellectual property forms the foundation of modern commerce. For Nigerian entrepreneurs, IP represents both protection for your innovations and opportunities for revenue generation through strategic licensing and commercialisation.
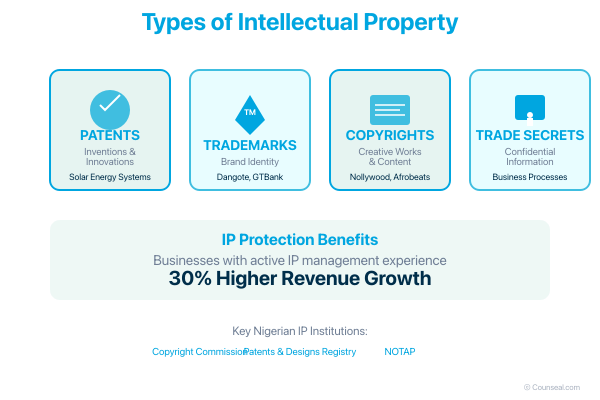
Types of Intellectual Property
Understanding the different categories of intellectual property helps you identify which protections apply to your business assets:
Patents
Patents protect inventions and technical innovations, granting exclusive rights to make, use, or sell your invention for up to 20 years. In Nigeria’s growing technology sector, patents protect everything from mobile payment systems to agricultural innovations. If you’ve developed a novel solar energy solution or manufacturing process, patent protection ensures competitors cannot replicate your innovation without authorisation.
Trademarks
Trademarks safeguard the distinctive symbols, names, and slogans that identify your goods or services. Think of how instantly recognisable brands like Dangote or GTBank become through consistent trademark use. Your business name, logo, and unique product names can all qualify for trademark protection, building brand recognition and customer loyalty.
Copyrights
Copyrights protect original creative works including literature, music, software code, and artistic expressions. Nigeria’s thriving creative industries—from Nollywood productions to Afrobeats music—demonstrate copyright’s commercial value. If you’ve developed proprietary software, written training materials, or created marketing content, copyright protection secures your ownership rights.
Trade Secrets
Trade secrets encompass confidential business information that provides competitive advantages. This might include customer lists, manufacturing formulas, or proprietary business processes. Unlike other IP types, trade secrets remain protected indefinitely—provided you maintain their confidentiality.
Why Protecting IP is Crucial for Nigerian Businesses
Intellectual property protection serves as both defensive strategy and growth catalyst. The World Intellectual Property Organisation reports that businesses actively managing their IP portfolios experience 30% higher revenue growth compared to those that don’t. This statistic reflects IP’s dual role: protecting your innovations whilst creating new revenue opportunities.
In Nigeria’s competitive business environment, IP protection prevents competitors from copying your innovations, preserves your market position, and enables monetisation through licensing agreements. Companies like Interswitch built their success partly through strategic IP management, protecting their payment processing innovations whilst licensing technology to expand market reach.
Understanding IP Licensing
IP licensing creates a contractual arrangement where you (the licensor) grant permission to another party (the licensee) to use your intellectual property under specified terms. Think of licensing as renting your innovations—you retain ownership whilst generating revenue from others’ use of your IP.
This arrangement differs fundamentally from selling your IP outright. When you sell, you transfer ownership completely, receiving a one-time payment but relinquishing future income potential. Licensing maintains your ownership rights whilst creating ongoing revenue streams through royalties or licensing fees.
Key Licensing Structures
Exclusive Licenses grant sole usage rights to one licensee, often commanding higher fees but limiting your ability to license to others. Non-exclusive licenses allow multiple licensees, spreading risk whilst potentially reducing individual licensing fees. Sole licenses fall between these extremes—granting rights to one licensee whilst preserving your own usage rights.
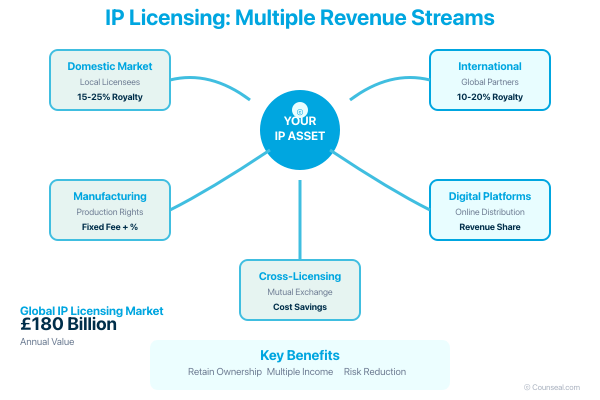
Cross-licensing arrangements involve mutual IP sharing between companies, particularly common in technology sectors where complementary innovations benefit both parties. Sublicensing permits your licensee to grant usage rights to third parties, extending your IP’s reach whilst requiring careful contract management.
Why Licensing and Commercialisation Matter for Business Growth
Monetising IP Assets
Your intellectual property represents untapped revenue potential. Rather than limiting your IP to internal use, licensing creates additional income streams without requiring significant operational expansion. The global IP licensing market, valued at £180 billion annually, demonstrates the substantial commercial opportunities available.
Nigerian businesses increasingly recognise IP licensing’s value. Fintech companies license payment processing technologies, creative professionals license content across multiple platforms, and manufacturers license production techniques to expand market presence without direct investment.
Expanding Market Reach
Licensing enables market expansion beyond your immediate operational capacity. Instead of establishing international offices or manufacturing facilities, you can partner with established companies possessing local market knowledge and distribution networks. This strategy proves particularly valuable for Nigerian businesses seeking African or global market entry.
Risk Reduction and ROI Maximisation
Licensing diversifies revenue sources, reducing dependence on single markets or products. Deloitte research indicates that businesses engaging in licensing experience 25% reduction in operational risks through revenue diversification. By sharing market development costs with licensees, you achieve returns on IP investments whilst maintaining ownership of valuable assets.
Strategic Approaches to IP Commercialisation
Direct Commercialisation
Direct commercialisation involves building your business around your IP, maintaining complete control over development, production, and marketing. This approach suits entrepreneurs with resources and market expertise to execute comprehensive business strategies. Innoson Vehicle Manufacturing exemplifies successful direct commercialisation, building Nigeria’s indigenous automotive industry around proprietary manufacturing technologies.
Licensing to Third Parties
Licensing offers revenue generation without operational complexity. You maintain IP ownership whilst partners handle production, marketing, and distribution. This strategy works particularly well for innovations requiring significant manufacturing investment or specialised market knowledge you may lack.
Joint Ventures and Partnerships
Joint ventures combine your IP with partners’ complementary assets—manufacturing capabilities, market access, or funding. These arrangements share both risks and rewards, enabling access to resources beyond your immediate capacity whilst maintaining significant control over IP application.
Franchising Models
Franchising systematically replicates your business model, combining trademark licensing with operational systems. This approach suits service-based businesses or retail concepts with proven success records, enabling rapid expansion through franchisee investment.
Essential Elements of Licensing Agreements
Scope and Duration
Clearly define what rights you’re granting—geographic territories, product categories, usage limitations, and time periods. Vague scope definitions create enforcement difficulties and potential disputes. Specify whether licensees can modify your IP, sublicense to others, or use it in combination with competing technologies.
Financial Terms
Structure compensation through upfront fees, ongoing royalties, or revenue sharing arrangements. Upfront payments provide immediate returns whilst royalties align your interests with licensee success. According to WIPO data, 67% of licensing agreements incorporate royalty structures, typically ranging from 2-15% of net sales depending on the industry and IP value.
Quality Control Provisions
Maintain standards protecting your IP’s reputation and value. Specify quality requirements, approval processes for product modifications, and regular monitoring procedures. Quality control provisions prove particularly crucial for trademark licensing, where poor product quality can damage your brand reputation.
Territorial Rights and Exclusivity
Define geographic boundaries and exclusivity terms clearly. Consider market size, licensee capabilities, and your expansion plans when structuring territorial arrangements. Exclusive territories often command higher fees but limit your flexibility for additional partnerships.
Regulatory Landscape for Nigerian Businesses
Nigerian IP Framework
Nigeria’s IP protection operates through several key institutions. The Nigerian Copyright Commission oversees copyright registration and enforcement. The Trademarks, Patents and Designs Registry handles trademark and patent applications. The National Office for Technology Acquisition and Promotion (NOTAP) regulates technology transfer agreements, requiring approval for international licensing arrangements involving foreign exchange.
Understanding these regulatory requirements prevents costly delays and ensures compliance with Nigerian law. NOTAP approval particularly affects international licensing deals, as non-compliance can restrict profit repatriation and create legal complications.
International Considerations
Nigerian businesses engaging in international licensing must navigate multiple jurisdictions’ requirements. Double taxation treaties with various countries can reduce tax burdens on international licensing income. The Paris Convention and Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) facilitate IP protection across multiple countries, streamlining international expansion strategies.
Get Expert Guidance on Your Nigerian Business Journey
Join 1000+ entrepreneurs who’ve transformed their Nigerian business plans with our strategic guidance. In one focused session, unlock:
- Market-ready opportunity assessment
- Regulatory compliance roadmap
- Implementation strategy tailored to your business
- Cost framework and resource planning
What You’ll Receive:
- Personalized Strategy Session with a Nigerian market specialist
- Custom Implementation Roadmap based on your specific business goals
- Regulatory Checklist tailored to your industry
- Priority Access to our implementation team when you’re ready
How It Works:
- Select your preferred time slot below
- Complete a brief business assessment
- Join your private Zoom session
- Receive your actionable implementation plan
Limited availability — Only 8 sessions offered each week
Tax Implications
Nigerian royalty income faces 10% withholding tax, whilst VAT applies at 7.5% on licensing services. These taxes affect pricing strategies and profit calculations. International licensing may qualify for reduced tax rates under double taxation treaties, making professional tax advice essential for optimising financial outcomes.
Common Challenges and Best Practices
Finding Suitable Partners
Identifying appropriate licensees requires thorough market research and due diligence. Evaluate potential partners’ financial stability, market reputation, and alignment with your business values. Industry associations, trade shows, and professional networks provide valuable partner identification resources.
Protecting IP Rights
Monitor licensee compliance through regular audits and quality assessments. Implement clear reporting requirements and maintain active surveillance for unauthorised usage. Technology solutions like digital watermarking and monitoring services help track IP usage across multiple platforms and territories.
Negotiating Fair Terms
Successful negotiations balance your interests with licensee needs. Professional negotiators or IP attorneys provide valuable guidance through complex discussions. Research comparable licensing deals to establish fair market rates and terms, ensuring agreements reflect your IP’s true value.
Financial Valuation and Analysis
IP Valuation Methods
Three primary approaches guide IP valuation: Cost-based methods calculate development expenses and replacement costs. Market-based approaches compare similar IP transactions and licensing rates. Income-based valuations project future earnings potential and calculate present value of expected returns.
Effective valuation often combines multiple approaches, providing comprehensive assessment of your IP’s worth. Professional appraisers specialising in IP valuation ensure accuracy and credibility for licensing negotiations and financial planning.
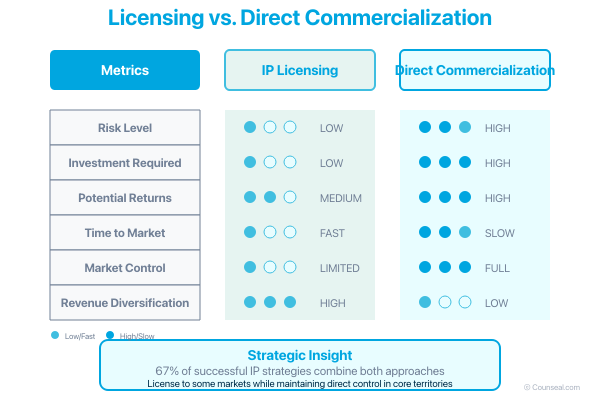
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Compare licensing revenue potential against direct commercialisation opportunities. Licensing typically offers lower risk and investment requirements but may provide lower total returns. Direct commercialisation requires substantial investment but offers greater profit potential and market control.
Consider your resources, risk tolerance, and strategic objectives when choosing between approaches. Many successful businesses employ mixed strategies, licensing to certain markets whilst maintaining direct operations in core territories.
Case Studies: Nigerian IP Success Stories
Fintech Innovation
Nigerian fintech companies demonstrate IP licensing’s potential through payment processing technologies. By licensing core technologies to banks and service providers, these companies expand market reach whilst maintaining technological leadership. Regulatory compliance and security requirements make licensing particularly attractive for financial services IP.
Creative Industries
Nollywood and Nigerian music industries showcase copyright licensing success. Film producers license content to international streaming platforms, reaching global audiences whilst maintaining ownership rights. Musicians license tracks for advertisements, films, and digital platforms, creating multiple revenue streams from single creative works.
Manufacturing and Technology
Nigerian manufacturers increasingly license production technologies and processes. These arrangements enable capacity expansion without capital investment whilst ensuring quality standards and operational efficiency. Technology licensing proves particularly valuable for companies serving both domestic and regional African markets.
Strategic Implementation Framework
Assessment and Protection
Begin with comprehensive IP audits identifying all protectable assets within your business. Secure appropriate registrations through relevant Nigerian authorities, ensuring your rights are legally established before pursuing licensing opportunities.
Market Analysis
Research potential markets, competitors, and licensing opportunities within your industry. Identify companies that could benefit from your IP whilst possessing complementary capabilities for successful commercialisation.
Partnership Development
Develop relationships with potential licensees through industry networking, trade associations, and professional connections. Quality partnerships often emerge from established business relationships and mutual trust.
Agreement Structure
Work with experienced IP attorneys to draft comprehensive licensing agreements protecting your interests whilst enabling partner success. Clear terms prevent disputes and ensure productive long-term relationships.
Monitoring and Enforcement
Establish systems for ongoing compliance monitoring and IP protection. Regular communication with licensees and proactive market surveillance help maintain your IP’s value and prevent unauthorised usage.
Looking Forward: The Future of IP in Nigeria
Nigeria’s growing digital economy creates expanding opportunities for IP licensing and commercialisation. Government initiatives supporting innovation and technology transfer encourage businesses to develop and monetise intellectual property assets.
The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) presents unprecedented opportunities for Nigerian businesses to license IP across African markets. Understanding IP protection frameworks across African countries enables strategic expansion through licensing partnerships.
Emerging technologies like blockchain and artificial intelligence create new IP categories and commercialisation models. Forward-thinking businesses are positioning themselves to capitalise on these developments through strategic IP development and protection.
Conclusion
Licensing and commercialising intellectual property offers Nigerian entrepreneurs powerful tools for business growth and market expansion. By understanding IP fundamentals, regulatory requirements, and strategic implementation approaches, you can transform innovative ideas into sustainable competitive advantages.
Success requires systematic approach—from initial IP identification and protection through strategic partnership development and ongoing relationship management. Professional guidance from IP attorneys, business advisors, and industry experts proves invaluable throughout this journey.
Your intellectual property represents more than legal protection—it embodies innovation, creativity, and commercial potential. Through strategic licensing and commercialisation, you can unlock this potential whilst building sustainable business growth.
The opportunities are substantial, the frameworks are established, and the market is ready. The question isn’t whether you should explore IP licensing and commercialisation—it’s how quickly you can begin transforming your intellectual assets into commercial success.
For expert guidance on protecting and commercialising your intellectual property, visit counseal.com/start to begin your IP strategy development today.





